Homology directed repair (HDR) is a mechanism in cells to repair double-strand DNA lesions. The most common form of HDR is homologous recombination. The HDR mechanism can only be used by the cell when there is a homologous piece of DNA present in the nucleus, mostly in Gand S phase of the cell cycle. Other examples of homology-directed repair include single-strand annealing and breakage-induced replication. This homologous sequence can then be used as a template for DNA repair synthesis that bridges the DSB.

In eukaryotic cells, mechanistic repair of DSBs occurs primarily by two pathways: Non-Homologous End-Joining (NHEJ) and Homology Directed Repair (HDR). NHEJ is the canonical homology-independent pathway as it involves the alignment of only one to a few complementary bases at most for the re-ligation of two ends, whereas HDR uses longer stretches of sequence homology to repair DNA lesions. Using Homology-Directed Repair for Targeted Integration HDR is a DSBR that uses a double-stranded DNA donor that has homology to the adjacent sequences surrounding the lesion to incorporate new DNA fragments. HDR offers more precision than NHEJ and allows for seamless integration of DNA. The earliest studied HDR pathway is HR.
Homology-directed repair (HDR) and other pathways for the repair of double-strand breaks (DSBs). This template can come from within the cell during late S phase or Gphase of the cell cycle, when sister chromatids are available prior to the completion of mitosis. There are main pathways that the cells follow to repair the break: non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) and homology-directed repair (HDR). As its name implies, the NHEJ pathway joins DSB ends without the need for a homologous template.

Although Cas9-mediated genome editing has been widely used to engineer alleles in animal models of human inherited diseases, very few homology-directed repair (HDR)–based genetic editing systems have been established in postnatal mouse models for effective and lasting phenotypic rescue. Homology Directed Repair Template (HDR) Template Preparation Homology Directed Repair Templates can be prepared by PCR amplification of a region of genomic DNA centered around the location of the desired modification. PCR products are then inserted and joined into a vector backbone.
Improving homology-directed repair efficiency in human stem cells. In the second part of this webinar, Justin McDonough, Ph Scientist at The Jackson Laboratory for Genomic Medicine, describes methods he and his colleagues have used to improve HDR efficiency in human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). The subsequent repair of chromosomal DSBs by the cell can be classified into two categories of repair pathways: non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) and homology-directed repair (HDR). At its core, NHEJ-break ends can be ligated without a homologous template, whereas HDR-breaks requires a template to guide repair. Working like genetic scissors, the Casnuclease opens both strands of the targeted sequence of DNA to introduce the modification by one of two methods.
Knock-in mutations, facilitated via homology directed repair (HDR), is the traditional pathway of targeted genomic editing approaches. Facilitating homology - directed repair for precise genome engineering in rice. Read the full article in plant biology recently published in Communications Biology. Homology - directed repair (HDR) and other pathways for the repair of double-strand breaks (DSBs). DNA double-strand breaks repaired by non-homologous end joining display limited DNA end-processing and chromosomal mobility.
By contrast, double-strand breaks undergoing homology - directed repair exhibit extensive processing and enhanced motion. The molecular basis of this movement is unknown. A genetic assay for homology - directed repair To develop a quantitative assay for optimizing HDR in zebrafish, we sought to target a locus that could provide phenotypic and molecular data on allele conversion.
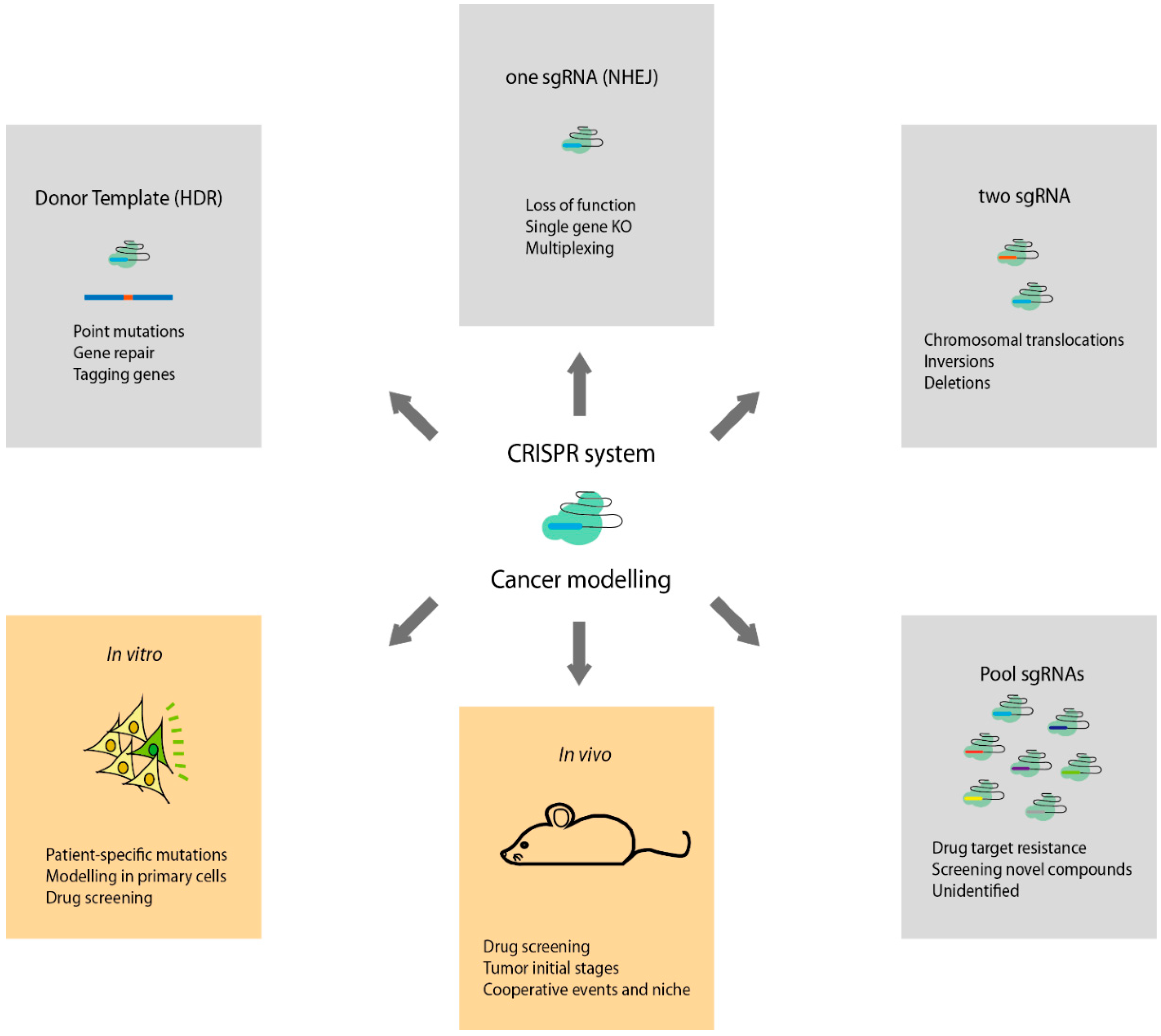
We initially examined the widely used mitfa (w2) mutant, which lacks melanocytes (29). The generation of point mutations is a major tool for evaluating the roles of specific nucleotides or amino acids within the regulatory or functional landscape. However, examination of these mutations in vivo requires the generation of animals carrying only the relevant point mutations at the endogenous genomic loci, which is technically challenging.
The CRISPR-Casbased genome editing. NHEJ is referred to as non-homologous because the break ends are directly ligated without the need for a homologous template, in contrast to homology directed repair , which requires a homologous sequence to guide repair.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.