This mechanism of repair only takes place only when DNA double stranded (duplex) contains extensive region of homology. As a result of this, the damaged DNA can access to the homologous area of duplex DNA and does a complementary pair of base pairing. Homologous Recombination Repair. HRR is a mechanism by which new haplotypes can arise from exchange of DNA sequence information between homologous , but not necessarily identical, chromosomes (Figure 3). It also provides a mechanism for the repair of double-strand breaks (DSBs) in DNA , where an intact DNA molecule is used as a template for the.
Resynthesis of the damaged region is accomplished using the undamaged molecule as a template. What is the role of recombination in DNA repair? How is homologous recombination repaired? Why does homologous recombination occur? Generally, homologous.
The initial steps of HR involve processing the DNA ends of DSBs by exonucleases to generate 3’ single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) tails (Figure 1). Two recombinases, Radand Dmc then form nucleoprotein filaments on ssDNA and search for DNA homologous sequences leading to strand invasion (D-loops in in vitro assay). In this era of translational medicine, clinical research is characterised by collaborations, all looking to. In general global response to DNA damage involves expression of multiple genes responsible for postreplication repair , homologous recombination , nucleotide excision repair , DNA damage checkpoint, global transcriptional activation, genes controlling mRNA decay, and many others.
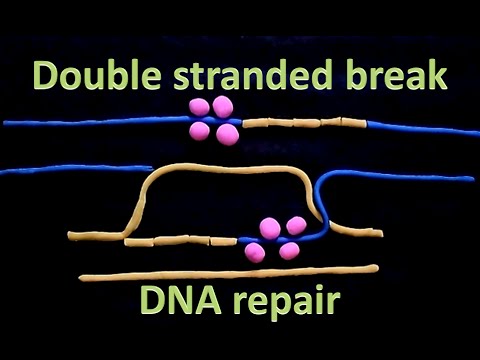
A large amount of damage to a cell leaves it with an important. The fact that failure to repair damaged DNA increases the possibility of developing tumors and other diseases highlights the importance of DNA repair. Presenter Kelompok (Penyanggah Kelompok 5): Topik Mutations2. The discovery that PARP inhibitors block an essential pathway of DNA repair in cells harbouring a BRCA mutation has opened up a new therapeutic avenue for high-grade ovarian cancers. BRCAand BRCAproteins are essential for high-fidelity repair of double-strand breaks of DNA through the homologous recombination repair (HRR) pathway.
It is most widely used by cells to accurately repair harmful breaks that occur on both strands of DNA , known as double-strand breaks (DSB). The repair system via homologous recombination repairs double-strand breaks (DSB) of DNA , which are the most mortal for cell, out of all DNA damages. The genes, which encode the double-strand break repairing proteins, are highly polymorphic an taking into account the significance of the repaired defects for cancer development, it seems.
DNA Recombination and Repair In cases where DNA is severely damage a cell will engage in a phenomenon called the SOS response in an effort to salvage a functioning set of genetic information. This response, also called error‐prone repair , represents a last‐ditch response to salvage a chromosomal information system. Deficiency in either of the breast cancer susceptibility proteins BRCAor BRCAinduces profound cellular sensitivity to the inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) activity.
We hypothesized that the critical role of BRCAand BRCAin the repair of double-strand breaks by homologous recombination (HR) was the underlying reason for this sensitivity. Determination of homologous recombination rate using the DR-GFP system indicate that SERBPdepletion reduced the rate of HR, comparable to the rate upon CtIP depletion. Here, we examine the effects of. To our knowledge, this is the first report that a component of HR-mediated DNA repair is regulated at the translational level. Now, researchers from Japan have identified mechanisms that choose between alternate.
The quintessential step in the recombination repair process. An invading strand displaces one strand of the homologous chromosome and base-pairs with the other. This allows the DNA to be repaired. Paired chromosomes from the male and female parent align so that similar DNA sequences from the paired chromosomes cross over each other. The role of DNA repair by homologous recombination in oncogenesis.
Fujinaka Y, Matsuoka K, Iimori M, Tuul M, Sakasai R, Yoshinaga K, Saeki H, Morita M, Kakeji Y, Gillespie DA,Yamamoto K, Takata M, Kitao H, Maehara Y. ATR-Chksignaling pathway and homologous recombinational repair. Looping the intervening DNA brings the duplicates together and allowing repair by homologous recombination. The measurement of homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) in cancer is therefore vital to the appropriate design of clinical trials incorporating PARP.
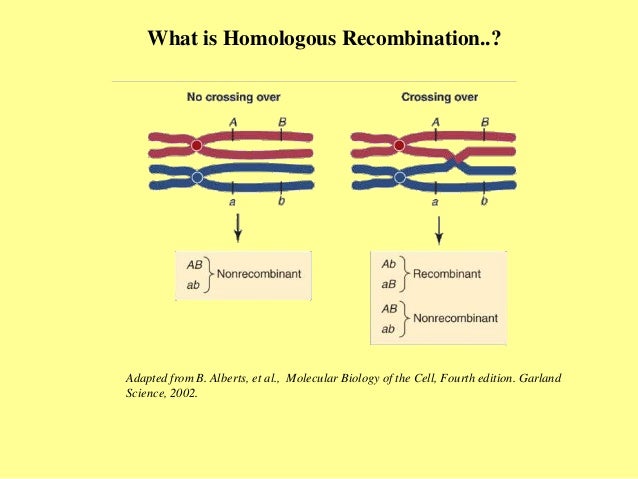
Recombination in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) was documented more than decades ago, but the underlying molecular mechanism has remained elusive.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.